What Is Total Shareholder Return (TSR)?
Dec 20, 2024 By Kelly Walker
Have you ever heard the term “total shareholder return” (TSR)? If not, don't worry - you're not alone. Total shareholder return is a measure of financial performance that considers both stock price appreciation and dividends received by shareholders for a specific period.
We'll break it down and discuss why TSR is so important when assessing company performance. We'll also explore how to calculate your own TSR and indices for using it effectively. By the end of this article, you should understand total shareholder return and how to use it to make informed decisions in your investing endeavors.
Total Shareholder Return (TSR)
Total shareholder return (TSR) is a measure of the financial performance of a company. It considers stock price appreciation and dividends shareholders receive for a specific period, usually one year. To calculate TSR, you take the sum of the capital gains - or losses - in the value of your shares plus any dividends paid out over that same period.
Total Shareholder Return Importance
Total shareholder return is important because it provides a comprehensive picture of a company's financial performance over a year. Unlike other measures such as earnings per share (EPS) or revenue, TSR considers both capital gains and dividends paid to shareholders - giving investors a more complete picture of their overall returns.
TSR is a great way to compare different companies or sectors in terms of their financial performance and the performance of individual stocks within those sectors.
By understanding total shareholder return, investors can make more informed decisions when selecting stocks and managing their portfolios. Analyzing TSR also provides insight into how a company has performed in the past year and can help predict how it may perform in future periods. This makes it an essential tool for investors looking to maximize their returns.
Calculation of Total Shareholder Return
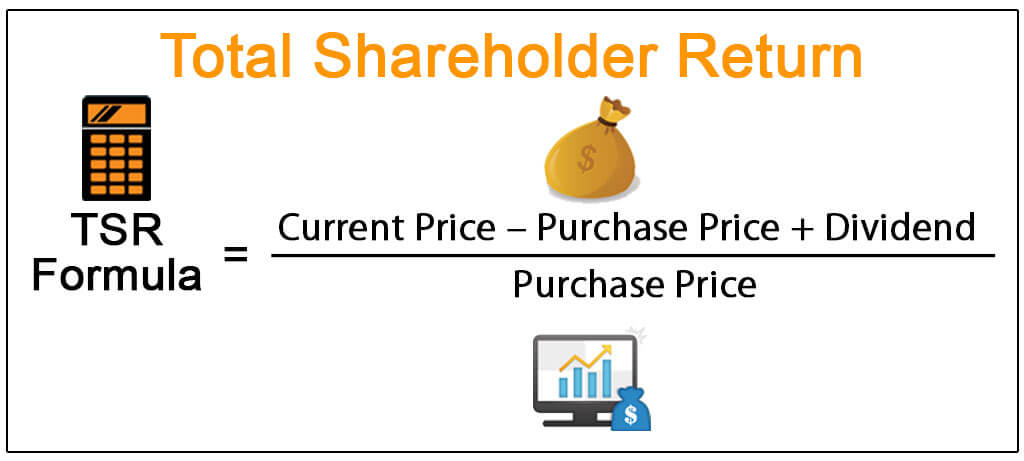
Calculating total shareholder return is relatively simple - all you need to do is add up the capital gains (or losses) in your stock plus any dividends paid out over a year. You'll need to know your stock's initial purchase and sale prices and any dividends paid over the period.
Once you have this information, calculating TSR is straightforward: just subtract the initial purchase price from the final sale price, then add any dividends received during that period. For example, if you purchased 100 shares of XYZ company at $10 each on January 1st and then sold them at $20 each on December 31st while receiving $1 per share in dividend payments throughout the year, your total shareholder return would be $900 ($1000 from capital gain + $100 from dividend payments).
Best Practices for Using Total Shareholder Return
When assessing a company's performance, it is important to consider the capital gains and dividends received over a year. This is why total shareholder return is such an important tool for investors. Here are some best practices for using TSR when analyzing a company:
- Analyze multiple periods: Analyzing a company's TSR over multiple periods is important to accurately understand its performance. This will also help you identify any trends or patterns that may be occurring.
- Consider other factors: While TSR provides useful information, it should not be used to determine a company's performance. Other factors, such as revenue growth, profitability, and market share, should also be considered when making investment decisions.
- Set goals: Setting specific goals for your investments can help you focus on achieving them over the long term. By setting goals and tracking your total shareholder return over multiple periods, you can more accurately measure your progress and make necessary adjustments.
- Diversify: Diversifying your portfolio is key to minimizing risk and maximizing returns. As part of this, it's important to diversify within and across sectors to ensure you are not overly exposed to any type of stock or industry.
- Monitor performance: Monitoring a company's total shareholder return over time can help you identify potential investment opportunities and areas needing improvement. By tracking TSR regularly, you can stay up-to-date with the performance of your investments and make informed decisions about when to buy or sell stocks.
By following these best practices, investors can use total shareholder returns to their advantage and maximize their returns.
Risks Involved with TSR Investing
While total shareholder return can be useful in evaluating a company's performance, some risks are also involved with TSR investing. Here are five of the most common:
- Market Risk: Since stock prices fluctuate and can be unpredictable, investors must know that their original investment may only sometimes yield positive returns. As such, it is important to factor market risk into any investment decision.
- Company Risk: Companies whose stocks you own could unexpectedly go out of business or face financial difficulty. This could lead to sizable losses if the investments are held until they become worthless.
- Inflation Risk: When calculating total shareholder return, it is important to consider inflation as stock prices and dividends may not increase at the same rate as inflation. This can lead to a decrease in the real value of your returns over time.
- Concentration Risk: Concentrating all or too much of your investment portfolio on one stock or sector could be risky because it may need to provide a diversified enough exposure.
- Dividend Cut Risk: Companies may reduce dividend payments due to financial difficulty. This could drastically reduce your total shareholder return and should be monitored closely.
Investors must understand that risks are always involved when investing in stocks and bonds. Still, with proper research and analysis, they can use total shareholder returns to make informed investment decisions.
FAQS
What does TSR mean by formula?
The formula for calculating TSR is (Current stock price + Dividends paid) / Initial investment. This will give you a percentage that shows the overall return provided by your initial investment, taking into account both stock appreciation and dividends received over a specified period.
How does TSR measure performance?
TSR measures the performance of an investment over a specified period by considering both stock price appreciation and dividend payments received. By tracking TSR regularly, investors can get an accurate indication of their returns and make informed decisions about when to buy or sell stocks.
What does TSR stand for in business?
TSR stands for Total Shareholder Return, a measure of financial performance that considers both stock price appreciation and dividends received by shareholders for a specified period. It evaluates the return on investments and helps investors decide when to buy or sell stocks.
Conclusion
Total Shareholder Return (TSR) is a key performance indicator that provides stakeholders with an understanding of how their investment has fared and their return on investment. Through TSR, investors can better understand how their money is doing and the company's overall financial health. Furthermore, it looks at the share price gain and the dividends paid to shareholders to give a comprehensive performance assessment over time.
On this page
Total Shareholder Return (TSR) Total Shareholder Return Importance Calculation of Total Shareholder Return Best Practices for Using Total Shareholder Return Risks Involved with TSR Investing FAQS What does TSR mean by formula? How does TSR measure performance? What does TSR stand for in business? Conclusion
Unlocking Six Best Free Checking Accounts

All You Should Know About Debt Related Statute of Limitations

Navigating Escrow Challenges in Real Estate Transactions

How Does Pattern Day Trading Work?

Steps to Making a Profit in Crude Oil Trading

Everything You Should Know About Direct Tax?

Is My Credit Score Useful Outside the US?

What Is Shale Oil?

Credit Cards vs. Debit Cards: What’s the Difference?

Best Identity Theft Protection Services

Companies Owned by Disney
