What Is Shale Oil?
May 18, 2025 By Kelly Walker
Have you ever heard of shale oil but needed to figure out what it is? If so, you're not alone. With the growing focus on alternative energy production and utilization sources, it's worth understanding how this unconventional type of hydrocarbon-rich rock can produce fuel. 
In this blog post, we'll explore what shale oil is, where and how it's extracted, how different methods are employed in its extraction process, and the many potential benefits and drawbacks of using this resource for energy production. Read on to learn more!
Shale Oil
At its core, shale oil is an unconventional type of hydrocarbon-rich rock. It’s found in sedimentary rocks such as shale and mudstone and is composed of organic matter that contains a significant amount of liquid petroleum or natural gas.
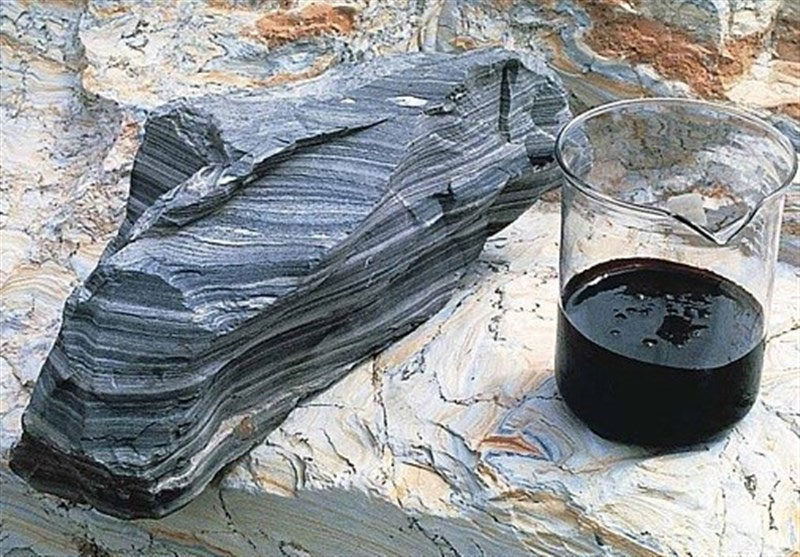

Unlike traditional crude oil, which can be easily accessed from the Earth's surface, shale oil is found in deeper sedimentary rock layers, typically between 900 and 3000 meters below the surface.
Shale oil extraction techniques have been used for decades but have become increasingly important due to technological advancements, allowing shale oil to be extracted more efficiently.
Currently, there are three main methods used in the shale oil extraction: hydraulic fracturing (or “fracking"), horizontal drilling, and in-situ thermal extraction.
Origin of shale oil?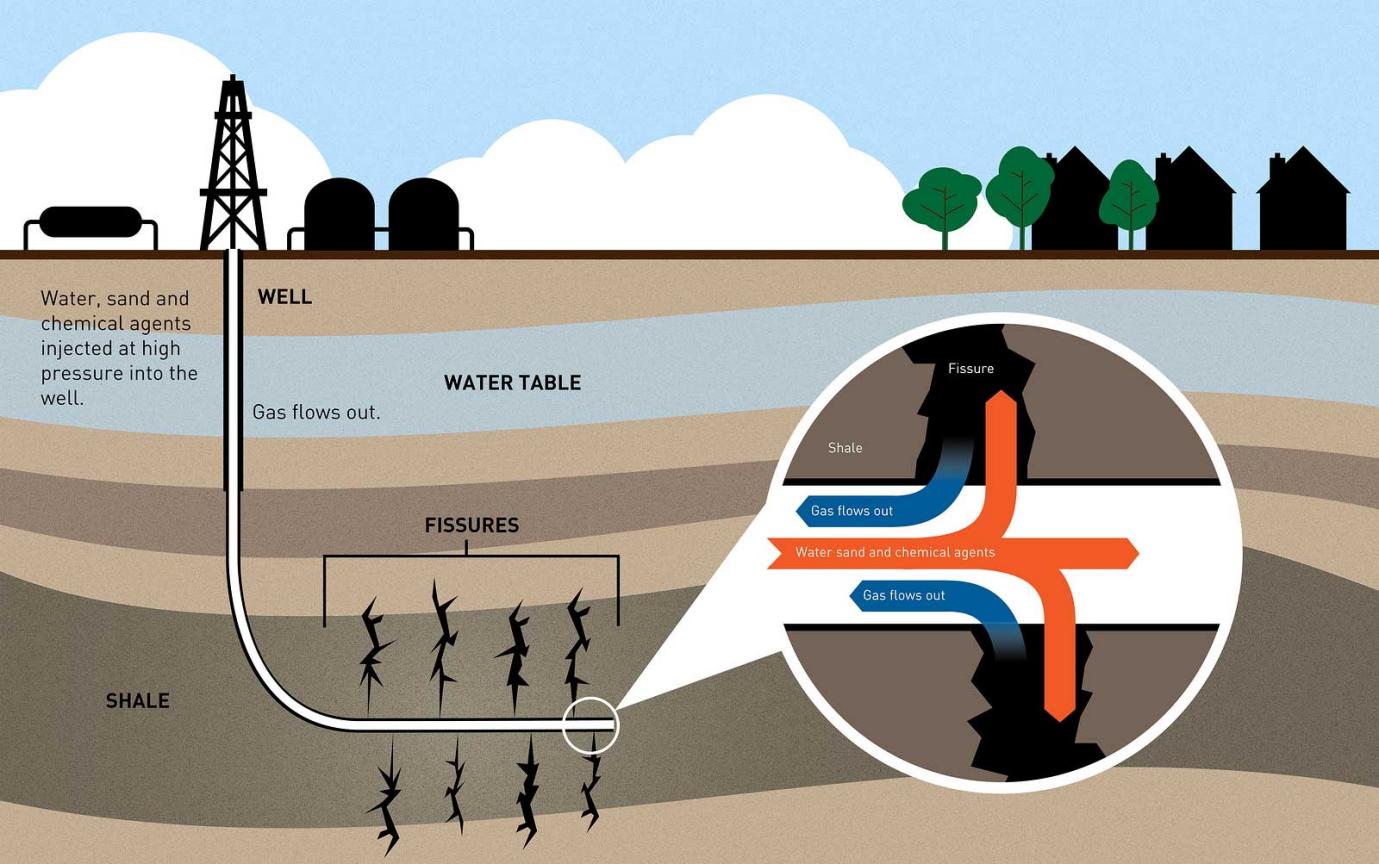
Shale oil is a naturally occurring resource formed over millions of years as organic matter and sediment mixed with liquid petroleum or natural gas. It’s found in sedimentary rocks such as shale and mudstone and can be extracted through various methods.
How Is Shale Oil Extracted?
The extraction process for shale oil involves drilling into the rock and then using a combination of techniques to release the hydrocarbons.
The three most common methods for shale oil extraction are hydraulic fracturing (or “fracking”), horizontal drilling, and in-situ thermal extraction.
Hydraulic fracturing is a process that uses pressurized liquid to break apart the shale rock and release the oil or gas. Horizontal drilling involves boring a wellbore horizontally instead of vertically, allowing more efficient access to the hydrocarbons trapped in shale.
In-situ thermal extraction is an energy-intensive process that uses heat to extract the oil from the shale by heating it to its boiling point.
Benefits of Shale Oil for the Environment:
1. Shale oil extraction is less energy-intensive than other oil production methods and thus has a lower carbon footprint
2. The process of hydraulic fracturing involves using water, sand, and chemicals which can reduce water contamination compared to traditional crude oil production techniques.
3. Unlike traditional crude oil, shale oil can be extracted from deeper depths, reducing the impact on surface land, wildlife, and habitats
4. Shale oil extraction has a much lower risk of oil spills or other environmental disasters that can occur with traditional crude extraction methods.
Challenges of Producing Shale Oil:
While shale oil production offers many potential benefits, it also presents several challenges. One major area for improvement is the location of the resources, which are often in remote areas and difficult to access. Additionally, the extraction process can be costly and complex; due to the geology of shale deposits, different methods may need to be implemented for efficient production.
Finally, there is some environmental concern surrounding the production and use of shale oil, as there are potential risks associated with water contamination and air pollution.
How is shale oil used in Everyday Life?
Regarding how shale oil is used daily, the answer varies greatly depending on where you live. In countries such as the United States and Canada, some of the most common ways shale oil is used are for heating homes and businesses, powering vehicles, and running industrial processes.
As a result, this resource can play an important role in helping to reduce dependence on traditional fossil fuels.
In addition to these more practical applications, some shale oil projects are also being developed to generate electricity. In these instances, "shale gasification" is often employed.
This method involves heating the rock and extracting combustible natural gas from it. Once the gas is collected, it can be burned to produce electricity in a power plant.
How to Incorporate Shale Oil Into Your Home?
Though it may not be the most viable option for energy production in your home, shale oil can still be incorporated into your lifestyle in some ways. For example, if you own an outdoor grill or heat lamp, you can use shale oil as a fuel source instead of the traditional propane or natural gas options.
It is important to note that shale oil is much heavier than conventional fuels and requires specialized equipment to burn properly. Additionally, it should be used cautiously due to its flammability and toxicity.
Examples of Shale Oil:
Shale oil is an unconventional fossil fuel that can be extracted from sedimentary rock formations.
It is composed of hydrocarbons, including oil and natural gas, which are trapped within the rocks and must be extracted through a process known as hydraulic fracturing (or “fracking”). The most common types of shale oil include tight oil, oil shale, and tar sands.
Tight Oil: Tight oil is light crude oil found in deeply buried sedimentary rocks, such as sandstone or limestone. It can be extracted through fracking using horizontal drilling and high-pressure water/chemical mixtures to break apart the rock formations and free up the embedded hydrocarbons.
Oil Shale: Oil shale is a sedimentary rock that contains large amounts of kerogen, an organic material composed of hydrocarbons. It can be mined and then heated without oxygen to produce oil and gas. The process, however, is costly and energy-intensive.
Tar Sands: Tar sands are sand and clay mixtures that contain crude bitumen, a heavy hydrocarbon. This type of shale oil is typically extracted through surface mining or steam-assisted gravity drainage methods.
FAQs
What does shale oil mean?
Shale oil is an unconventional type of petroleum, which is found in fine-grained sedimentary rocks called shale. This resource has been used as a energy source for many years and is becoming increasingly popular due to its potential benefits.
Where is it found?
Shale oil can be found worldwide, including in North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. It is typically found in sedimentary basins rich in organic material - meaning they contain large amounts of ancient plant and animal remains.
Why is shale oil expensive?
Shale oil extraction requires specialized processes and technologies, which can be expensive. In addition, the resource itself is often located in remote areas that are hard to access, making production more costly.
Conclusion:
Shale oil is an unconventional hydrocarbon-rich rock that can be used to produce fuel. There are several methods for extracting shale oil, each with potential benefits and drawbacks. Because of this, it's important to consider both the ecological and economic implications before deciding if shale oil is the right choice for energy production.
While it can positively affect the environment, it's important to keep in mind the costs associated with extracting shale oil, as well as any potential environmental impacts that could result from its extraction and use.
Ultimately, whether or not shale oil is the right choice for energy production will depend on various factors and should be carefully weighed before a decision is made.
On this page
Shale Oil Origin of shale oil? How Is Shale Oil Extracted? Benefits of Shale Oil for the Environment: How is shale oil used in Everyday Life? How to Incorporate Shale Oil Into Your Home? Examples of Shale Oil: FAQs What does shale oil mean? Where is it found? Why is shale oil expensive? Conclusion:
The Basics of Commodity Futures: A Beginner's Guide

What Is Shale Oil?

Understanding Tax Benefits

Is It Possible? Transferring Your Mortgage to Another Borrower

10 Essential Steps to Prepare Your House for Sale

Steps to Making a Profit in Crude Oil Trading

High-Value Home Insurance: What is it?

How Does Pattern Day Trading Work?

Unlocking Six Best Free Checking Accounts

Understanding Whole Life and Universal Life Insurance: Which Is Right for You?

Top Biotech Stocks
